Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles- MCQ Online Test 1 Class 9 Maths
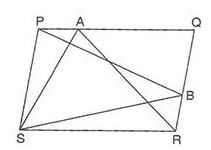
1. PQRS is a parallelogram and A and B are any points on PQ and QR. If ar(║;PQRS) = 48cm2, then ar(△PBS) +ar(△ASR) is equal to
(a) 48cm2
(b) 40cm2
(c) 45cm2
(d) 37cm2
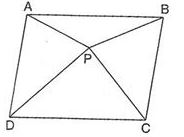
2. In the given figure ABCD is a parallelogram and its area is 64cm2. If P is any point in the interior of ║ABCD, then ar (△APD) +ar(△PBC) is equal to
(a) 38cm2
(b) 40cm2
(c) 32cm2
(d) 50cm2
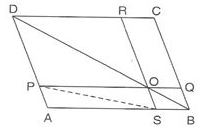
3. ABCD is a parallelogram. O is any point on diagonal BD. If ar(△DOP) = 8cm2, ar(△BOS) = 3cm2 and ar(△APS) = 6cm2,then ar(║ABCD) is
(a) 40cm2
(b) 36cm2
(c) 46cm2
(d) 42cm2
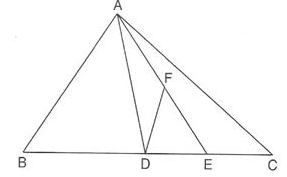
4. ABC is a triangle in which D is the mid-point of BC. E and F are mid-points of DC and AE respectively. If ar(△ABC)=16cm2, then ar(△DEF) is
(a) 6cm2
(b) 5cm2
(c) 4cm2
(d) 2cm2
5. The median of a triangle divides it into two
(a) isosceles triangles
(b) triangles of different areas.
(c) right angles.
(d) congruent triangles.
6. A, B, C, D are mid-points of sides of parallelogram PQRS. If ar(PQRS) = 36cm2, then ar (ABCD) is
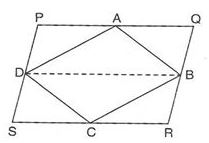
(a) 28cm2
(b) 18cm2
(c) 20cm2
(d) 24cm2
7. PQRS is a trapezium with PQ║SR. A line parallel to PR intersects PQ at X and QR at Y. If ar(△PYR) = 5cm2,then ar(△PXS) is
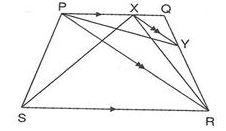
(a) 15cm2
(b) 5cm2
(c) 9cm2
(d) 8cm2
8. ABCD is quadrilateral whose diagonal AC divides it into two parts, equal in area, then ABCD
(a) is a rectangles
(b) is a rhombus
(c) is a parallelogram
(d) need not be any of (a), (b) or (c).
9. The altitude of a parallelogram is twice the length of the base and its area is 1250cm2. The lengths of the base and the altitude respectively are :
(a) 22 cm, 51 cm
(b) 20 cm, 40 cm
(c) 25 cm, 50 cm
(d) 35 cm, 53 cm
10. Two parallelograms are on equal bases and between the same parallels. The ratio of their areas is
(a) it is 3 : 4
(b) it is 2 : 1
(c) it is 1 : 2
(d) it is 1 : 1
Class 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles Quiz - 1Time limit: 0
Quiz-summary0 of 10 questions completed Questions:
Information
Click on ‘Start Quiz’ to Take Test. You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again. Quiz is loading... You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz: Results0 of 10 questions answered correctly Your time: Time has elapsed You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0) Categories
|